close
close
 close close
|
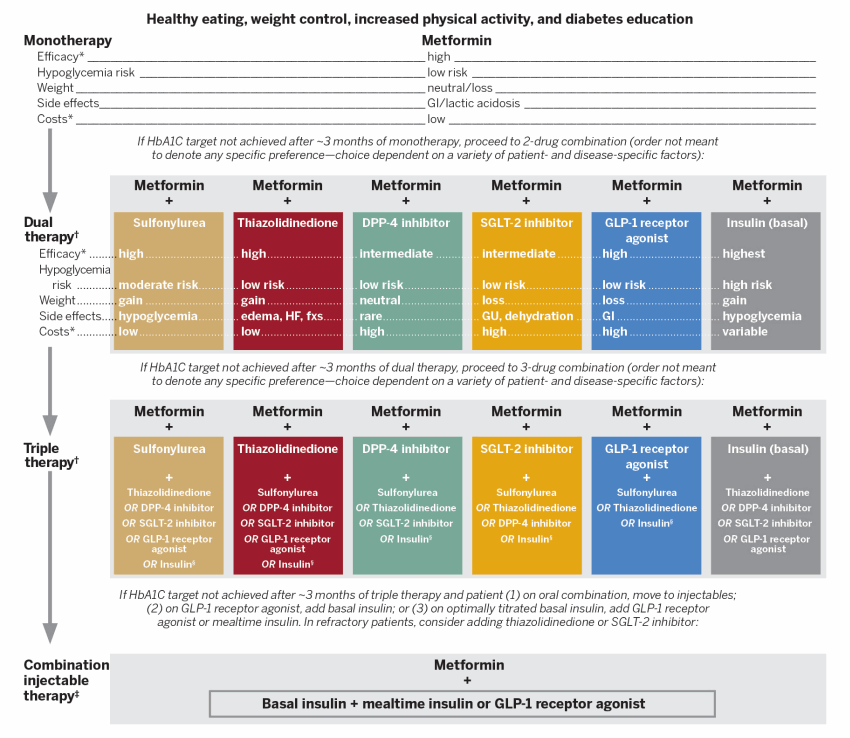
FIGURE 4. The American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes Algorithm for Determining Combination Therapy
†Consider initial therapy at this stage when glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) ≥ 9% (≥ 75 mmol/mol). |